cs144 lab1: stitching substrings into a byte stream 预备知识:《计算机网络自顶向下方法》——3.4 可靠数据传输原理
复习下如何构造一个可靠数据传输协议,书中是基于三种假设,逐层递进地讲解的。
rdt1.0:该协议假设底层信道完全可靠
rdt2.0:该协议假设底层信道不可靠,但仅仅会导致 datagram 的比特位出错,而不会导致任何丢失
rdt3.0:该协议假设底层信道完全不可靠,既会导致 datagram 的比特位出错,也可能导致整个包丢失
对于 rdt1.0,没啥好说的。
rdt2.0 该协议要应对存在 bit 出错的可能,因此引入了以下功能:
对于 rdt2.0 由于会存在 bit 出错的情况,因此引入一个 checksum,根据查错纠错算法和 checksum 来判断接收到的 datagram 是否有 bit 出错。
如果存在 bit 出错,那么接收方就要发送一个 NACK 给发送方,用来表示 “你发了的信息在途中遭到了破坏!请重新发送!”;如果没有 bit 出错,那么接收方就发一个 ACK 给发送方,用来表示 “我接受到了你发的信息!” 其实这里还有一个需要考虑的地方,那就是:接收方必须能够分辨出,接收到的 datagram 是发送方重传的还是最新的! 这里可以引入一个 1 bit 的序号 ,每次发送新的信息时进行 0,1 转换就可以分辨出发来的是新消息还是重传的消息了。
发送方,发送/重传一个消息后,必须等待接收方的反馈。并根据接收方的反馈做出具体的操作。如果收到 ACK,则发送新消息,并把新消息中的序号位反转一下以表示新消息;如果是 NACK,那么就重传旧消息。
rdt3.0 该协议不仅仅要应对 bit 出错的情况,还要应对分组丢失的情况,因此在 rdt2.0 的基础上又引入了以下功能:
由于发出去的消息可能在网络中丢失,那么如果让发送方不断地等待接收方的反馈,可能会导致等到地老天荒也没等来反馈。这是如果引入一个定时器,如果在规定的时间内没有收到反馈就可以简单地认为 datagram 在网络中丢失了!那么发送方就对旧消息进行重传。
但是可能信息并没有丢失,而是网络太拥堵导致它迟到了,而此时发送方已经重传了,那么这会导致冗余分组。
总结下:checksum,序号,ACK,定时器和重传 等技术确保了在不可靠网络上进行可靠传输。
缝合字符串 回归主题,本次 lab 就是为之后的 TCPReceiver 做准备的。
主要是设计一个 StreamReassembler 把字符串碎片重新组合成一个有序的字节流 ByteStream,首先对字符碎片进行定义:
字符碎片取自 ByteStream
字符碎片 A 和字符碎片 B 可能重叠
当字符碎片可以被 assemble 时立刻组装并交付给 ByteStream
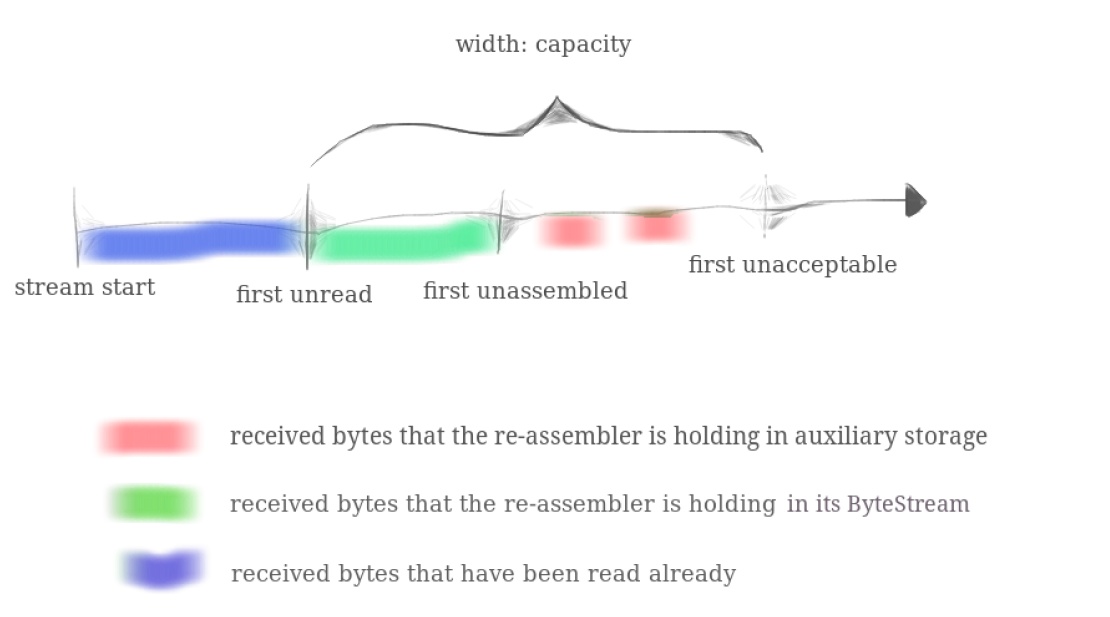
可以参考下面的图:
对于第一个定义,它想表达的是字符碎片是 ByteStream 的子串。
对于第二个定义,如果 ByteStream = “abcdefghi” 那么 A、B 可能是:A = “bcde”、B = “def”;即 A和B之间存在重叠。
对于第三个定义,什么情况下字符碎片可以被 assemble?那就是当前字符碎片的 index 是 rcv_base 的时候(这个 rcv_base 请去看《计算机网络自顶向下》3.4.4 节 图 3-23)。举个例子,我们已经收到字符碎片 A 和 B了(A、B的值和上面一样),那么可以把A 和B合并成 “bcdef”,但是由于现在的 rcv_base = 0,也就是 “a” 的index,所以不能 assemble;直到 rcv_base = 1 时我们才能把 “bcdef” 交付给 ByteStream。
就像上图,first unassembled 到 first unacceptable 的区间内,可以看到一段一段的红色,每一段都表明了一个被合并过的字符碎片,每个字符碎片都是 ByteStream 的子串。而绿色的是已经有序且连续的但未被读走的 ByteStream 子串。
其实这里就已经有 TCP 接收缓冲区(对应 ByteStream) 以及滑动窗口(对应 StreamReassembler) 的感觉了!
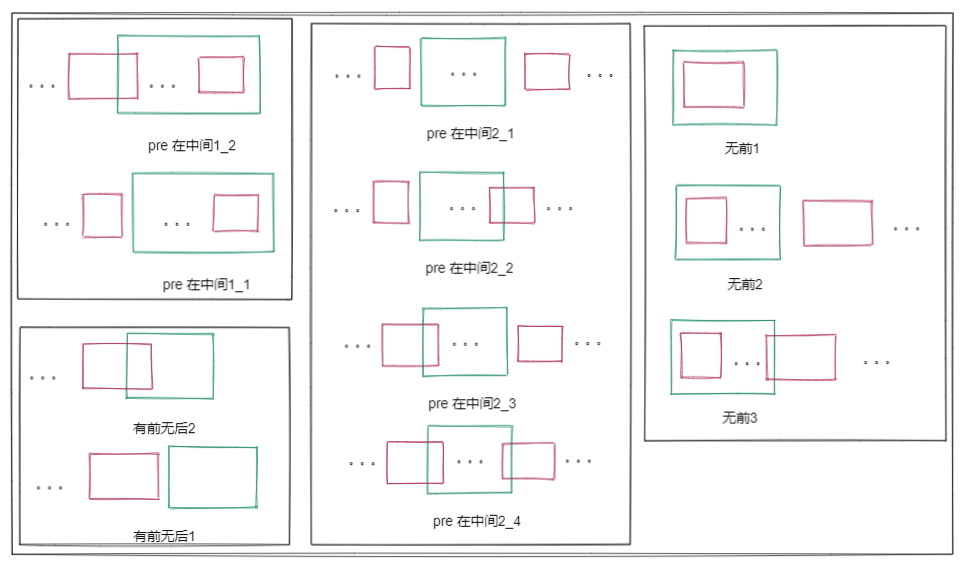
在代码实现方面,最难的是如何对接收到的字符串碎片 与已经存储在 first unassembled 到 first unacceptable 的区间内的字符串碎片 进行合并 ,这个合并涉及到了对碎片的去重叠。所以说这个 lab 更像是在做一道算法题。。。。。。
这个算法可以参考,OS 对内存页回收时要进行操作,它也要判断是否可以和前后页进行合并!但这里更加复杂,内存页的合并只需要考虑前一个页与后一个页,而这里需要考虑多个字符串碎片,因为可能存在 A = “bcd”、B = “f”、C = “hi” 然后收到了 “abcdefgh” 的情况~~~
可以把要进行合并(merge)的字符串碎片和合并会涉及到字符串碎片抽象成如下图所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 void StreamReassembler::merge (StreamReassembler::Node node) if (_aux_storage.size() == 0 ) { _aux_storage.insert(node); _unassembled_bytes += node.length; return ; } auto pre = _aux_storage.lower_bound(node); if (pre == _aux_storage.end()) { --pre; if (pre->end() < node.index) { _aux_storage.insert(node); update_unassembled_bytes(_aux_storage.end(), _aux_storage.end(), node); return ; } else if (pre->end() < node.end()) { std ::string tmp = *pre->spStr + node.spStr->substr(pre->end() - node.index); node.spStr.reset( new std ::string (std ::move(tmp)) ); node.index = pre->index; node.length = node.spStr->size(); _aux_storage.erase(pre); _aux_storage.insert(node); auto begin = pre; auto end = ++pre; update_unassembled_bytes(begin, end, node); } } else if (pre == _aux_storage.begin()) { auto it = pre; while (it != _aux_storage.end()) { if (it->end() > node.end()) break ; ++it; } if (it == _aux_storage.end()) update_storage(_aux_storage.begin(), _aux_storage.end(), node); else if (it->index > node.end()) update_storage(pre, it, node); else { node.spStr.reset(new std ::string (*node.spStr + it->spStr->substr(node.end() - it->index))); node.length = node.spStr->size(); ++it; update_storage(pre, it, node); } } else { auto it = pre; while (it != _aux_storage.end()) { if (it->end() > node.end()) break ; ++it; } if (it == _aux_storage.end()) { auto t = --pre; if (t->end() < node.index) { ++t; } else { node.spStr.reset( new std ::string (*t->spStr + node.spStr->substr( t->end() - node.index ) ) ); node.index = t->index; } update_storage(t, it, node); } else { auto a = --pre; auto b = it; if (a->end() < node.index && node.end() < b->index) { ++a; } else if (a->end() < node.index) { node.spStr.reset( new std ::string (*node.spStr + b->spStr->substr( node.end() - b->index ) ) ); node.length = node.spStr->size(); ++a; ++b; } else if (node.end() < b->index) { if (a->end() >= node.end()) return ; node.spStr.reset( new std ::string (*a->spStr + node.spStr->substr( a->end() - node.index ) ) ); node.index = a->index; node.length = node.spStr->size(); } else { node.spStr.reset( new std ::string (*a->spStr + node.spStr->substr( a->end() - node.index ) + b->spStr->substr(node.end() - b->index) ) ); node.index = a->index; node.length = node.spStr->size(); ++b; } update_storage(a, b, node); } } }
其他的代码都是很简单的逻辑啦~~~~
这里是功能定义:stream_reassembler.hh
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 class StreamReassembler {public : struct Node { Node(size_t idx, uint32_t l, std ::shared_ptr <std ::string > sp) : index(idx), length(l), spStr(std ::move(sp)) {} size_t index; uint32_t length; std ::shared_ptr <std ::string > spStr; size_t end () const return index + length; } }; struct NodeCmp { bool operator () (const Node& lhs, const Node& rhs) const return lhs.index < rhs.index; } }; private : using SetType = std ::set <Node, NodeCmp>; uint32_t _rcv_base{0 }; uint32_t _eof_index{0xffffffff }; uint32_t _unassembled_bytes{0 }; SetType _aux_storage; ByteStream _output; size_t _capacity; private : std ::pair <size_t , std ::string > get_valid_data(const std ::string & data, const size_t index); uint32_t remain_capacity () const return _capacity - _unassembled_bytes - _output.buffer_size(); } uint32_t update () void write_to_aux_storage (std ::pair <size_t , std ::string > p) void merge (Node node) void update_unassembled_bytes (SetType::iterator a, SetType::iterator b, const Node& node) uint32_t total = 0 ; for (auto it = a; it != b; ++it) total += it->length; _unassembled_bytes += node.length - total; } void update_storage (SetType::iterator a, SetType::iterator b, const Node& node) update_unassembled_bytes(a, b, node); _aux_storage.erase(a, b); _aux_storage.insert(node); } .... };
这里是实现:stream_reassembler.cc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 StreamReassembler::StreamReassembler(const size_t capacity) : _aux_storage(), _output(capacity), _capacity(capacity) {} void StreamReassembler::merge (StreamReassembler::Node node) void StreamReassembler::write_to_aux_storage (std ::pair <size_t , std ::string > p) std ::string tmp = p.second.size() > _capacity ? p.second.substr(0 , _capacity) : p.second; Node node (p.first, tmp.size(), std ::make_shared<std ::string >(tmp)) ; merge(node); } uint32_t StreamReassembler::update () auto it = _aux_storage.begin(); size_t writed = _output.write(*it->spStr); size_t ret = _rcv_base + writed; _unassembled_bytes -= writed; if (writed == it->length) { _aux_storage.erase(it); } else { Node node = {ret, it->length - static_cast <uint32_t >(writed), std ::make_shared<std ::string > (it->spStr->substr(writed)) }; _aux_storage.erase(it); _aux_storage.insert(node); } if (ret == _eof_index) _output.end_input(); return ret; } std ::pair <size_t , std ::string > StreamReassembler::get_valid_data(const std ::string & data, const size_t index) { if (index >= _rcv_base) return {index, data}; size_t end = index + data.size(); if (end < _rcv_base) return {0 , {}}; return {_rcv_base, data.substr(_rcv_base - index)}; } void StreamReassembler::push_substring (const string &data, const size_t index, const bool eof) if (eof) _eof_index = index + data.size(); auto p = get_valid_data(data, index); if (p.second.empty()) { if (_rcv_base == _eof_index) _output.end_input(); return ; } write_to_aux_storage(p); if (p.first == _rcv_base) { _rcv_base = update(); } else { } } size_t StreamReassembler::unassembled_bytes() const { return _unassembled_bytes; } bool StreamReassembler::empty () const return 0 == unassembled_bytes(); }
除此之外可以看看 Leetcode 56 题:
以数组 intervals 表示若干个区间的集合,其中单个区间为 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 。请你合并所有重叠的区间,并返回 一个不重叠的区间数组,该数组需恰好覆盖输入中的所有区间 。
示例1:
1 2 3 输入:intervals = [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]] 输出:[[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]] 解释:区间 [1,3] 和 [2,6] 重叠, 将它们合并为 [1,6].
示例2:
1 2 3 输入:intervals = [[1,4],[4,5]] 输出:[[1,5]] 解释:区间 [1,4] 和 [4,5] 可被视为重叠区间。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public : vector <vector <int >> merge(vector <vector <int >>& intervals) { vector <int > tmp; sort(intervals.begin(), intervals.end()); int start = intervals[0 ][0 ], end = intervals[0 ][1 ]; vector <vector <int >> ret; for (int i = 1 ;i < intervals.size(); ++i) { if (intervals[i][0 ] <= end) end = max(end, intervals[i][1 ]); else { ret.push_back({start, end}); start = intervals[i][0 ]; end = intervals[i][1 ]; } } ret.push_back({start, end}); return ret; } };